CS2103/T at a Glance
CS2103/T is an introductory Software Engineering module. It covers basic SE theory and practices that a student needs to know before doing SE internships in the industry or taking
On the theory side, this module is supported by a customized online text book Software Engineering for Self-Directed Learners, integrated into this module website.
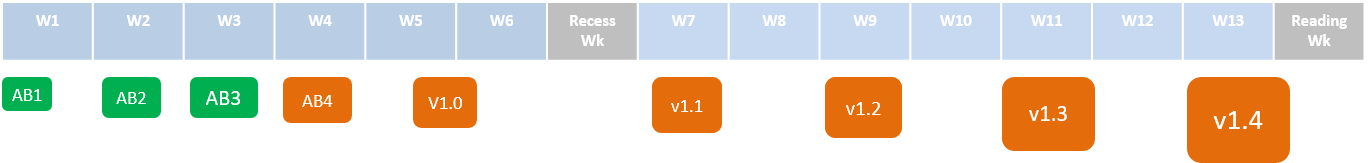
The practice side of this module is mainly covered by a team project. Students are expected to take over an existing project AddressBook-Level4 (AB4) -- a relatively small yet non-trivial (10 KLoC) generic product -- and enhance it into a better product or evolve into a different product. To help students to tackle the learning curve of working with 10 KLoC of code, the module takes them through a series of projects of increasing size, from AddressBook-Level1(1 KLoC) to AddressBook-Level3(4 KLoC).
Given below is a summary of what the module covers and does not cover (i.e., unticked items).
Java:
- Used heavily, but not taught
- syntax (reason: expected prerequisite knowledge)
OOP:
- Used in a non-trivial project,
intermediate OOP principles - basics (reason: expected prerequisite knowledge)
SE tools/practices:
-
those typically used in a mature, high-rigor SE project - those specific to start-ups
Modeling:
-
Some UML notations (sufficient to be able to describe SE artifacts using models, such as seen in this Developer Guide of AB4) - intensive
upfront design modeling
Requirements:
-
Some lightweight techniques to gather and document project requirements - rapid prototyping, heavy UI design, designing a product from scratch
Documentation
- Documentation targeting end users (example) as well as those targeting developers (example)
- Marketing materials
Project Management
- Iterative delivery of a product, Working collaboratively with team members, on-site as well as remotely
- Setting up project infrastructure from scratch
Testing
-
basic developer testing anduser testing -
testing for non-functional aspects
Applications domains:
- Cross-platform desktop applications
- Web programming, Mobile programming, Database programming